Many comment threads on this blog turn into discussions of same-sex marriage. Well here is a post where that conversation will be on point.
The Pew Foundation yesterday published a Q & A on the topic with “professors Robert W. Tuttle and Ira “Chip” Lupu of The George Washington University Law School to discuss how some states are trying to reconcile these and other potential conflicts between the legalization of gay marriage and the free exercise of religion.”
This is timely given the rush of legislatures in the northeast to enact same-sex marriage statutes. The latest news came from New Hampshire where the governor has threatened a veto unless a religious liberty clause is a part of the legislation. The sticking point is concern over the conscience rights of merchants to refuse to take part in ceremonies or activities involving gay marriage. Governor Lynch wants a wider set of exemptions and some gay marriage supporters want a narrow set of protections of conscience.
Year: 2009
Genetic effects of gender atypical behavior and sexual orientation: A study of Finnish twins
Due to time constraints, this post is less review than description of results. However, I wanted to post something on this study in advance of some commentary coming from Michael Bailey on the topic.
Here is the reference and abstract:
Abstract: The existence of genetic effects on gender atypical behavior in childhood and sexual orientation in adulthood and the overlap between these effects were studied in a population-based sample of 3,261 Finnish twins aged 33–43 years. The participants completed items on recalled childhood behavior and on same-sex sexual interest and behavior, which were combined into a childhood gender atypical behavior and a sexual orientation variable, respectively. The phenotypic association between the two variables was stronger for men than for women. Quantitative genetic analyses showed that variation in both childhood gender atypical behavior and adult sexual orientation was partly due to genetics, with the rest being explained by nonshared environmental effects. Bivariate analyses suggested that substantial common genetic and modest common nonshared environmental correlations underlie the co-occurrence of the two variables. The results were discussed in light of previous research and possible implications for theories of gender role
development and sexual orientation.
Common Genetic Effects of Gender Atypical Behavior in Childhood
and Sexual Orientation in Adulthood: A Study of Finnish Twins
K. Alanko, P. Santtila, N. Harlaar, K. Witting, M. Varjonen, P. Jern, A. Johansson, B. von der Pahlen, & N. K. Sandnabba. Arch Sex Behavior.
The sample was obtained via a registry maintained by the Central Population Registry of Finland which includes all twin pairs born in 1971 or earlier. The researchers requested information from the twins and received responses from 36% of those surveyed (3,604). For various reasons, the authors assume representativeness of their sample, although I think they might be open to some challenge on this point given the response rate.
The authors used Zucker’s Recalled Childhood Gender Identity/Gender Role Questionaire and Sell’s Assessment of Sexual Orientation. The SASO assesses both behavior and attractions via four items:
Item 1: During the past year, on average, how often were you sexually attracted to a man (woman for female participants)? The response alternatives were: never, less than 1 time per month, 1–3 times per month, 1 time per week, 2–3 times per week, 4–6 times per week, daily. Item 2: During the past year, on average, how often did you have sexual contact with a man (woman for female participants)? The response alternatives were the same as for Item 1 above. Item 3: How many different men (women for female participants) have you had sexual contact with during the past year? Item 4: During the past year, on average, how many different men (women for female participants) have you felt sexually attracted to? The response alternatives to Items 3 and 4 were: none, 1, 2, 3–5, 6–10, 11–49, 50–99, 100C. The participants were given numerical scores so that a response of ‘‘none’’/‘‘never’’ gave a score of 0 and a response of ‘‘100 or more’’/‘‘daily’’ gave a score of 7.
Here are the correlations of twins sharing traits of sexual orientation and gender atypical behavior.
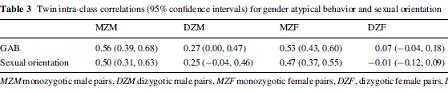
Correlations were higher for identical twins than fraternal twins for both traits, especially for women. About the genetic contribution to GAB and sexual orientation, the authors said:
Significant genetic effects were found for women and men for both GAB and sexual orientation, as was our second hypothesis. The heritability estimates for childhood GAB were 51% and 29%, and for sexual orientation 45% and 50%, for women and men, respectively.
These numbers are higher than past studies and may be related to the nature of the sampling although this is not clear.
The authors also found a relationship between GAB and sexual orientation.
Our first aim was to study the phenotypic correlations between childhood GAB and adult sexual orientation. Significant correlations of moderate sizes were found, indicating that the two phenomena were related. The strength of the phenotypic association was higher for male participants, implying that childhood GAB was a stronger predictor of adult sexual orientation for men.
The authors note that these data in conjunction with past studies lead them to propose the possibility of several pathways to homosexual attractions.
There might, in other words, be different genotypes for different kinds of homosexuality. It might also be possible that the relative importance of shared environment and genetic influences vary during development. It is plausible that parents influence their children directly only as long as they live at home (Knafo et al., 2005; Plomin et al., 2001). Bailey et al. (2000) found that GAB predicted about 30% of the variance in men’s sexual orientation. As neither the phenotypic nor the genetic correlations were unity in the present sample, GAB preceded a homosexual orientation for some participants, whereas gender typicality preceded a homosexual orientation for other participants.
What did not show up was any significant role of shared environment for men. A small amount of the effect could be attributed to shared environment for women. Another data point suggesting that the pathways to adult sexual orientation are different for men and women.
Stay tuned…
Parenting, homosexuality and gender atypical behavior
Over the next several days, I am going to comment on lots of new research out of Finland. Here is a preliminary post with a result sure to be surprising to some.
First the reference and abstract:
Alanko K, Santtila P, Witting K, Varjonen M, Jern P, Johansson A, von der Pahlen B, Kenneth Sandnabba N., Psychiatric Symptoms and Same-Sex Sexual Attraction and Behavior in Light of Childhood Gender Atypical Behavior and Parental Relationships,
J Sex Res. 2009 Apr 2:1-11. [Epub ahead of print]
This study explores the relation between the level of current symptoms of depression and anxiety and recalled childhood gender atypical behavior (GAB), and quality of relationships with parents among men and women who reported same-sex sexual attraction or engaged in same-sex sexual behavior and men and women who did not. Matched pairs, 79 men (n = 158) and 148 women (n = 296), with equal levels of GAB were created of Finnish participants with either same-sex sexual attraction or behavior and participants without. The measures used were retrospective questionnaires. Ratings of maternal and paternal over-control and coldness differed as a function of same-sex sexual attraction or behavior. Childhood GAB was correlated with negative ratings of parental relationships. Both same-sex sexual attraction or behavior and a history of childhood GAB affected the reported levels of current depression and anxiety. Only gender typical participants with no same-sex sexual attraction or behavior reported significantly lower levels of symptoms. The findings suggest that childhood GAB is related to later distress both among hetero- and homosexual individuals. The elevated level of psychological distress among homosexual individuals, reported in several studies, might-to some extent-be caused by their generally higher levels of childhood GAB as opposed to a homosexual orientation per se.
The study investigated 3 hypotheses. They were:
1. Childhood GAB is related to a negative parent-child relationship.
2. Homosexual orientation is related to a negative parent-child relationship.
3. Childhood GAB, more than current sexual orientation, predicts the level of current psychiatric symptoms.
This study emerges from an ongoing research program at the Center of Excellence for Behavior Genetics, Department of Psychology, Abo Akademi University in Turku, Finland. I will have more to say about the entire study in later posts, I want to lead off with one of the more provocative findings of this paper.
Regarding their fathers, the authors found that gay males reported warmer relationships than straight males. The researchers stated,
A distant (cold) relationship with the father of gay men was expected on the basis of previous studies; however, in this study, gay men reported warmer paternal, as well as maternal, relationships than heterosexual men did.
There is more to report here but that one will get us started. I am tracking down the instrument used to assess relationship warmth which will demonstrate more clearly what the modest differences signify.
Overall, the study finds that GAB also relates to negative parenting and current distress whether the participants were gay or straight. The GAB factor may help unravel some of the findings of poorer mental health outcomes previously reported for gays and lesbians.
Preview of coming attractions
Here is a preview of posts for the next couple of weeks.
1. New research – Commenter Evan pointed out two new studies of interest, one a twin study and the other related to the the role of gender atypical behavior in adult mental distress. In additional to those two papers, there are two other studies on childhood gender nonconformity that I want to review as well.
2. Q&A with Michael Bailey – Dr. Bailey will comment on the new Finnish twin study. He will also speak about the mistakes those on the right and left make in interpreting these studies.
3. Rebuttal to the Pink Swastika – I will be providing a guest post, a difficult to locate response to arguments which form the basis for the Pink Swastika and primary sources which contradict Scott Lively’s view that the Nazism was animated by homosexuality.
I suspect those posts will lead to several follow ups that should keep us busy.
WorldNetDaily suddenly finds year old NARTH article newsworthy
A reader emailed me to say that the American Psychological Association had recently changed the official view on homosexuality causation to endorse an environmental set of causes. The prompt for the email was this article from WorldNetDaily: “‘Gay’ gene claim suddenly vanishes”
To arrive at this startling conclusion, the WND writer, Rob Unruh quotes an article published more than a year ago from NARTH titled, “APA’s New Pamphlet On Homosexuality De-emphasizes The Biological Argument, Supports A Client’s Right To Self-Determination.”
In the article, Dean Byrd notes that the APA document shifts emphasis on causes to a more nuanced and complex view. Byrd cites this quote:
“There is no consensus among scientists about the exact reasons that an individual develops a heterosexual, bisexual, gay or lesbian orientation. Although much research has examined the possible genetic, hormonal, developmental, social, and cultural influences on sexual orientation, no findings have emerged that permit scientists to conclude that sexual orientation is determined by any particular factor or factors. Many think that nature and nurture both play complex roles…”
However, oddly, Byrd leaves this last phrase from the APA website out of his quote:
…most people experience little or no sense of choice about their sexual orientation.
Also in the APA paper, reparative therapy is discussed. The APA says
What about therapy intended to change sexual orientation from gay to straight?
All major national mental health organizations have officially expressed concerns about therapies promoted to modify sexual orientation. To date, there has been no scientifically adequate research to show that therapy aimed at changing sexual orientation (sometimes called reparative or conversion therapy) is safe or effective. Furthermore, it seems likely that the promotion of change therapies reinforces stereotypes and contributes to a negative climate for lesbian, gay, and bisexual persons. This appears to be especially likely for lesbian, gay, and bisexual individuals who grow up in more conservative religious settings.
Helpful responses of a therapist treating an individual who is troubled about her or his same-sex attractions include helping that person actively cope with social prejudices against homosexuality, successfully resolve issues associated with and resulting from internal conflicts, and actively lead a happy and satisfying life. Mental health professional organizations call on their members to respect a person’s (client’s) right to self-determination; be sensitive to the client’s race, culture, ethnicity, age, gender, gender identity, sexual orientation, religion, socioeconomic status, language, and disability status when working with that client; and eliminate biases based on these factors.
From these paragraphs expressing concern, Byrd pulls out this sentence to portray a greater openness to change therapy than is warranted:
“Mental health organizations call on their members to respect a person’s [client’s] right to self-determination.”
I blogged about this article last year when it came out, commending the APA for their nuanced account of the research to that point. I think NARTH should do what the APA did a year ago and issue a statement about environmental causes. Then I wondered:
…when NARTH would make an APA-like statement about theorized environmental factors such as child abuse and same-sex parenting deficits. What if NARTH acknowledged “what most scientists have long known: that a bio-psycho-social model of causation best fits the data?” Wouldn’t there be a need for a statement cautioning readers of their materials that evidence for parenting playing a large or determining role is meager? Paralleling Dr. Byrd’s assessment of the APA pamphlet, shouldn’t NARTH say with italics, “There is no homogenic family. There is no simple familial pathway to homosexuality.”…
I wrote Dean and asked him about NARTH’s stance. He answered for himself by saying,I think that the bio-psycho-social model of causation makes it clear that there is neither a simple biological or environmental pathway to homosexuality.
NARTH is widely known for championing a view of homosexuality that requires some kind of trauma as a causal factor. In point of fact, SSA can occur without bad parenting or abuse. Shouldn’t NARTH follow the APA’s lead and issue an official statement such as suggested above?
UPDATE: OneNewsNow and AFTAH have joined the echo chamber.
The ONN account begins:
The attempt to prove that homosexuality is determined biologically has been dealt a knockout punch. An American Psychological Association publication includes an admission that there’s no homosexual “gene” — meaning it’s not likely that homosexuals are born that way.
I wonder if NARTH will correct this misunderstanding of the APA’s publication. In fact, no knockout punch has been delivered to any theory, except perhaps for those dogmatic views that stress one pathway. Let’s see leaving aside extreme biological determinism, who else gets a knockout punch here? The APA statement cuts both ways but NARTH, and the people quoted in this report only want to see it go one way.
The APA (over a year ago) handled the research with integrity. When will NARTH and related groups do the same?