Class, when you see the phrase “new scientific research,” what comes to mind?
What would you expect to read?
What would make you think, ‘hey look there – new scientific research’?
What is New. Scientific. Research?
A college psychology professor's observations about public policy, mental health, sexual identity, and religious issues
Class, when you see the phrase “new scientific research,” what comes to mind?
What would you expect to read?
What would make you think, ‘hey look there – new scientific research’?
What is New. Scientific. Research?
The Southern Voice has an article regarding the recent breathless, echo-chamber enhanced series of articles from some conservative blogs and news services about changes in the American Psychological Association statement regarding sexual orientation.
As I noted here awhile back, the recent flurry was not new news. My first blog about it was when NARTH’s Dean Byrd produced an article for the NARTH website.
In the Sovo article, the APA’s Clinton Anderson seems bemused by the far right response to something they did over a year ago.
Clinton Anderson, director of the APA’s lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender concerns office, said the change was so subtle that “from our perspective, there really hasn’t been any change.”
But some conservative groups have hailed the wording change as apparent affirmation that sexual orientation is not genetically defined.
Peter LaBarbera, president of Americans for Truth about Homosexuality, said the reason “so many people in the pro-family movement are delighted by this is that it seems to confirm our doubts that there’s a gay gene, that homosexuality is inborn.”
“A lot of gay activists have used the idea of genetic homosexuality as a convenient argument to further their case,” he said. “This makes it harder for them to do that, because they can chastise the religious right, but it’s harder for them to chastise the APA.”
I still wait for NARTH to issue a similar position statement regarding the nature of homosexuality – multiple factors, multiple pathways, we don’t know how any of this works very well, etc.
Instead NARTH trumpets a paper saying that research leads to a conclusion that homosexuality is not innate – despite the absence of any evidence to support the “conclusion” in the paper.
In graduate school, I read and thoroughly enjoyed Jerome Kagan’s The Nature of the Child. I have excerpted the beginning of chapter 7 below as a means of continuing the conversation about the relevance of childhood events for sexuality. This chapter is titled, “The Role of the Family” and the excerpt comes from pages 240-242.
I have said little about the influence of experience on the child, especially the consequences of parental behavior. The most important reason for this omission is that the effects of most experiences are not fixed but depend upon the child’s interpretation. And the interpretation will vary with the child’s cognitive maturity, expectations, beliefs, and momentary feeling state. Seven-year-old boys who are part of a small isolated culture in the highlands of New
Guinea perform fellatio regularly on older adolescent males for about a half-dozen years; but this behavior is interpreted as part of a secret, sacred ritual that is necessary if the boy is to assume the adult male role and successfully impregnate a wife (Herdt, 1981). If an American boy performed fellatio on several older boys for a half-dozen years, he would regard himself as homosexual and possess a fragile, rather than a substantial, sense of his maleness.
Children growing up in Brahmin families in the temple town of Bhubaneswar in India hear their mothers exclaim each month, “Don’t touch me, don’t touch me, I’m polluted.” These children do not feel rejected or unloved, because they know this command is a regular event that occurs during the mother’s menstrual period (Shweder, in press). And a small proportion of American children, whose affluent parents shower them with affection and gifts out of a desire to create in them feelings of confidence and self-worth, become apathetic, depressed adolescents because they do not believe they deserve such continuous privilege.
As these examples make clear, the child’s personal interpretation of experience, not the event recorded by camera or observer, is the essential basis for the formation of and change in beliefs, wishes, and actions. However, the psychologist can only guess at these interpretations, and the preoccupations and values of the culture in which the scholar works influence these guesses in a major way. For example, Erasmus (1530), who believed the child’s appearance reflected his character, told parents to train the child to hold his body in a controlled composure – no furrowing of brows, sagging of cheek, or biting of the lip, and especially no laughter without a very good cause.
Educated citizens in early sixteenth-century London, who were disturbed by the high rate of crime, begging, and vagrancy among children of the poor, blamed the loss of a parent, living with lazy parents, being one of many children, or a mental or physical handicap. These diagnoses ignored the possible influence of genetics, parental love, or social conditions existing outside the home. Two centuries later, a comparable group of English citizens concerned with identical social problems, but still without any sound facts, emphasized the influence of the love relation between mother and child (Pinchbeck and Hewitt, 1969 and 1973).
Many contemporary essays on the influence of family experience also originate in hunches, few of which are firmly supported by evidence. This is not surprising; the first empirical study to appear in a major American journal that attempted to relate family factors to a characteristic in the child was published less than sixty years ago in The Pedagogical Seminary (Sutherland, 1930). The fact that a hunch about the role of family originates in a society’s folk premises about human nature does not mean that it is incorrect. Eighteenth-century French physicians believed that a nursing mother should bathe the baby regularly and not drink too much wine – suggestions that have been validated by modern medicine. But those same doctors also believed – mistakenly, I suppose – that cold baths will ensure a tough character in the older child. The absence of conclusive evidence means that each theorist must be continually sensitive to the danger of trusting his or her hunches too completely, for at different times during the last few centuries of European and American history, the child has been seen as inherently evil, or as a blank tablet with no special predispositions, or, currently, as a reservoir of genetically determined psychological qualities. Modern Western society follows Rousseau in assuming that the infant is prepared to attach herself to her caregiver and to prefer love to hate, mastery to cooperation, autonomy to interdependence, personal freedom to bonds of obligation, and trust to suspicion. It is assumed that if the child develops the qualities implied by the undesirable members of those pairs, the practices of the family during the early years – especially parental neglect, indifference, restriction, and absence of joyful and playful interaction – are major culprits.
I cannot escape these beliefs which are so thoroughly threaded through the culture in which I was raised and trained. But having made that declaration, I believe it is useful to rely on selected elements in popular theory, on the few trustworthy facts, and on intuition in considering the family experiences that create different types of children, even if my suggestions are more valid for American youngsters than for those growing up in other cultures.
Kagan refers to Gilbert Herdt’s book, Guardians of the Flutes, published in 1981 which describes the masculinity rituals of the Sambian tribe (not the actual tribal name) in Papua New Guinea. Essentially the tribe “believes” boys become men by ingesting the semen (“male milk”) of older boys. And of course, by the teen years, it “works” and the boys attain manhood. At that point, the vast majority of males choose a female partner.
Kagan’s reference to this practice reminds us that these experiences are embedded in a culture. In our own, such experiences would not be normalized and contextualized as a contributing to masculinity but rather detracting from it.
I cannot improve on Kagan’s description of his thesis. He is a gifted writer. However, I will elaborate for sake of discussion. He proposes that perception drives the psychological impact of a given experience. How differing perceptions effect the development of sexuality seems to me to be highly individualistic. Thus, for some, sexual maltreatment might push an essentially heterosexual person toward same-sex preoccupations. For others, abuse might strengthen the budding heterosexual impulses toward heterosexual preoccupations. For others, the abusive events may have no effect on attractions but rather influence attachment security. My point here is not to describe all possible trajectories, but rather to illustrate the potential of many variations.
A related point made by Kagan is that our culture looks at parenting as causative of adult personality. I believe many people do not question this assumption. In the last several years, I have looked for data to support or contradict it. I find little support that individual personality traits or conditions are strongly related to particular family dynamics. However, some broad trends can be observed. Fatherlessness is associated with a variety of problems in children and society. However, not having a father around may be interpreted in different ways by different children. For some, having the wrong kind of father around might lead to anti-social behavior. Thus, simply isolating childhood variables and relating them to adult outcomes is insufficient. These points are often lost on reparative therapists and other advocates who want to reduce homosexuality to a set of family dynamics or childhood experiences. On the other hand, biological determinists err on the side of discounting these social experiences as potentially influential for some people.
A satisfying position to me is to consider homosexual behavior to be determined by different factors in different ways for different people. For some, there is a very early awareness of romantic and sexual attraction for the same-sex independent of any trauma or parenting actions. For others, trauma and poor parenting occur but the same-sex attractions appeared prior to these unhappy events. For yet others people, the unhappy experiences may serve to create a disconnect between impulse to same-sex behavior and internal desire and attraction which may be toward the opposite sex. While these complexities create PR problems for culture warriors on both sides, I believe we must recognize the existence of multiple pathways to adult sexuality if we are to be true to the data and experience.
The role of child sexual abuse in sexual orientation has received some attention lately. In January of this year, a prospective study demonstrated that child sexual abuse was associated with ever engaging in adult homosexual behavior for males but not for females. The study by Widom and Wilson demonstrated that physical abuse or neglect did not associate with homosexuality, nor did sexual abuse predict same-sex cohabitation or current sexual partner. In other words, measures of behavior (living with a same-sex partner ever, or living with one in the last year) that would be more reflective of orientation were not associated with histories of child sexual abuse. For males, ever engaging in homosexual behavior, however, was associated with sexual abuse. Many observers are not surprised by this finding which indicates that sexual behavior is associated with past abuse but enduring orientation may not be.
Prospective studies are quite valuable since they help control for loss of memory, reconstructed memories, self-report issues relating to abuse and other sources of bias. This study used court records and followed up the abused persons 30 years after the fact.
In evangelical circles, sexual abuse is frequently offered as a major cause of homosexuality, if not the major cause. NARTH often points to the traumatic experience as an important factor. Recently, Focus on the Family promoted a paper by Jeff Johnston on the topic. Cited by Dean Byrd in that paper and often cited in this context is a study based on a 2000 doctoral dissertation by Marie Tomeo, titled “Sexual Orientation Development” and conducted at the California School of Professional Psychology. The journal article based on the dissertation was published by the Archives of Sexual Behavior in 2001 with the following reference:
Tomeo, M. E., Templer, D. L., Anderson, S., & Kotler, D. (2001). Comparative data of childhood adolescence molestation in heterosexual and homosexual persons. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 30, 535–541.
The study compared people at a gay pride parade with a straight sample drawn primarily from a university. The abstract reports the highlights:
In research with 942 nonclinical adult participants, gay men and lesbian women reported a significantly higher rate of childhood molestation than did heterosexual men and women. Forty-six percent of the homosexual men in contrast to 7% of the heterosexual men reported homosexual molestation. Twenty-two percent of lesbian women in contrast to 1% of heterosexual women reported homosexual molestation. This research is apparently the first survey that has reported substantial homosexual molestation of girls. Suggestions for future research were offered.
Demonstrating a difference between gay and straight groups on sexual abuse is not novel. Numerous studies have reported at least some difference with only a few reporting no difference in abuse frequency between groups. However, Tomeo did something that was relevant to her overall dissertation topic. She was interested in exploring sexual abuse as a potential causal factor. Tomeo’s prime research hypothesis was that homosexuals would report more sexual abuse than heterosexuals. She also wanted to know when a person identified as gay and when the abuse occurred. This is an important question for studies which seek to attribute cause to abuse. With some people being aware of same-sex attraction at very early ages, one cannot say any subsequent abuse caused their SSA. Simply finding a significant difference between gay and straight groups cannot tell you anything definitive about cause. Here are the first nine questions Tomeo asked her participants:
1. Do you regard yourself as predominantly a heterosexual person or predominantly a gay/lesbian person?
2. If predominantly of heterosexual orientation, at what age did you begin to regard yourself as heterosexual?
3. If predominantly of homosexual orientation, at what age did you begin to regard yourself as homosexual?
4. Before you were 16 years old, did you ever have sexual contact with a woman or girl 5 or more years older than yourself and at least 16 years of age? (YES NO)
5. IF YES, at what age did this first occur?
6. What was your relationship to the person with whom this sexual contact occurred?
7. Before you were 16 years old, did you ever have sexual contact with a man or boy 5 or more years older than yourself and at least 16 years of age? (YES NO)
8. IF YES, at what age did this first occur?
9. What was your relationship to the person with whom this sexual contact occurred?
For a study of causation, these questions clearly have their limitations. For one thing, when one regards oneself as homosexual probably occurs later (sometimes much later) than awareness of same-sex attraction. Perhaps one could offer a theory of identity formation which includes sexual abuse but such a theory would not of necessity be a theory of how one’s attractions take the direction they do.
In Tomeo’s reporting of her study in both the dissertation and the journal article, however, there is a much larger concern. There are contradictions in the paper and the dissertation between the results sections and the discussion sections. A crucial problem is the inability to be certain about when the abuse occurred – before or after awareness of same-sex attraction. In the Archives of Sexual Behavior article, the following statement is made on pages 540-541 (this same statement is identical to her closing discussion in the dissertation):
Sixty-eight percent of the present homosexual male participants and 38% of the present homosexual female participants (68 and 36%, respectively, if including just the homosexual fair participants) did not identify as homosexual until after the molestation. This suggests that if molestation resulted in homosexuality, this phenomenon occurs in a greater proportion of male homosexuals. It may not, however, be a casual factor in either gender. Perhaps children or adolescents with a higher potential for homosexual behavior are more likely to enter a situation that leads to same-sex molestation. It must also be borne in mind that the present homosexual participants may not be representative of homosexual persons. The overwhelming preponderance of homosexual participants was in the gay pride group. There were only three homosexual men and seven homosexual women in the college group.
The clear implication in this discussion section is that the frequency of homosexual identification was a consequence of the abuse. However, in the table which reported the data regarding timing of identification, the authors report the same percentage of males who reported identification as gay before the abuse. Table II on page 538 reports (click the link for a clearer view):
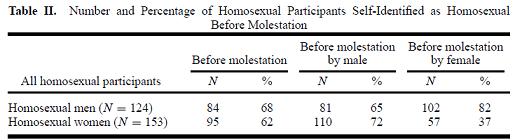
Something is not right here. If the table is correct, then the case for causation from this study is somewhat compromised. The table indicates that 68% of men identified as homosexual before their molestation experience.
My colleague Gary Welton and I first discovered this discrepancy nearly three years ago while preparing a scholarly article on the effects sizes of various suggested correlates of homosexuality (one which will be published later this year or early next year). At that time, I contacted Donald Templer, one of the co-authors and advisor to first author Marie Tomeo. I then contacted him again recently in preparation for this post. He has been unable to locate Dr. Tomeo to get clarification. I hope Dr. Tomeo can at some point clarify these matters.
Recently, I ordered the dissertation to check the original study. However, there are discrepancies in this document as well. First, here are the relevant research questions with results.
From page 36 of Marie Tomeo’s dissertation:
The 10th research question addressed, of homosexual women who were molested, what percentage were molested before self-identification as a homosexual woman and what percentage were molested after self-identification as a homosexual woman? Of homosexual women who were molested, 62% were molested before self-identification as a homosexual woman, and 38% were molested after self-identification as a homosexual woman.
On page 37, the other relevant result relates to men.
The 13th research question addressed, of homosexual men who have been molested, what percentage were molested before self-identification as homosexual men, and what percentage were molested after self-identification as homosexual? Of homosexual men who were molested, 68% were molested before self-identification as homosexual, and 32% were molested after self-identification as homosexual.
These results are at odds with the discussion sections of the dissertation and the journal. They are also at odds with the Table from the journal article. For what its worth, Dr. Templer thinks the correct data are in the Table from the journal article.
The bottom line is that the study should not be cited until a follow up correction can be made. The main results — gays report more abuse than straights — may indeed be correct, given the similarity to past studies. However, I do not believe any inferences about causation should be made. Without the actual surveys, there is no way a reader can figure out the results from the journal article and/or the dissertation.
One final thought, the research on sexual abuse among GLBT populations is often misused to make inferences about causation. There are many reasons why this line of research is important but causation is not at the top. Sexual abuse is a profoundly disruptive experience for many people and may contribute to a variety of negative outcomes in adulthood. Finding appropriate clinical and ministry responses may be clouded by focusing on the trauma as a cause of same-sex attraction.
Through the end of June, the Archives of Sexual Behavior is available to the public via the publisher’s Reading Room website.
This is a limited opportunity to get access to full text articles at no cost. Different journals are featured each quarter and in this case ASB was selected as a featured journal. Just a note, I had trouble accessing the feature via Mozilla Firefox, but have had no trouble using Internet Explorer.
Happy reading!