In the first part of my review of the NARTH fact sheet on female homosexuality, I critiqued the empirical foundation of the NARTH theories about causation of female same-sex attraction.
In this post, I examine the statements regarding sexual abuse and causation. It may be surprising to some observers to read this:
Although sexual abuse does not directly cause same sex attraction, studies report male sexual abuse of lesbians as generally being twice as high as of heterosexual women, that is, on average, 50 percent of lesbian women report a history of sexual abuse. (26, 27) If family relational dynamics and gender nonconformity are already in place, sexual abuse can clench the direction of detachment, gender insecurity, and disidentification possibly leading to same sex attraction.
The article does not specify sexual abuse as a direct cause of same-sex attraction. However, the author does believe that being abused as a child can push a girl in that direction if she suffered detachment from her mom and was gender nonconforming as a child.
I checked the references offered by NARTH for the assertion that sexual abuse of lesbians by men are “twice as high as of heterosexual women” and that “50 percent of lesbian women report a history of sexual abuse.” I cannot find these statistics.
Reference 26 is to a survey of lesbians, gay men, and bisexuals and their siblings by Balsam, Rothblum, and Beauchaine in 2005 (see reference list at the end of the post). In this study, the authors used a convenience sample of same-sex attracted people and asked them to recruit a sibling to participate. They reported childhood sexual abuse (CSA) prevalences for straight (30.4%), lesbian (43.6%) and bisexual (47.6%) female participants. The effect size of these differences are very low, between 1-2%.
Reference 27 is to research reported in the Journal of Gay and Lesbian Social Services by Hughes and team in 2000. In this study, forty-one percent of lesbians reported CSA while among straight women the number was 24%.
The NARTH article adds:
Sexual abuse can be emotional, verbal, or physical. A girl who is sexually objectified though inappropriate sexual comments, denied age appropriate privacy or whose father has voyeuristic tendencies, has been sexually violated without ever being touched. (28, 29)
I do not contest that the paternal behaviors referenced here are inappropriate and potentially harmful. However, the references for these statements does not provide research support for the statements about CSA. One, (29) is not to a research study but to a book for a lay audience by Janette Howard and the other (28) is a 1991 research study by Peters and Cantrell which failed to discriminate lesbians and straight women via abuse variables.
There are some discouraging percentages in this literature but they apply to women overall, with a moderate elevation for lesbians. Here is what I found in a brief PsychLit search.
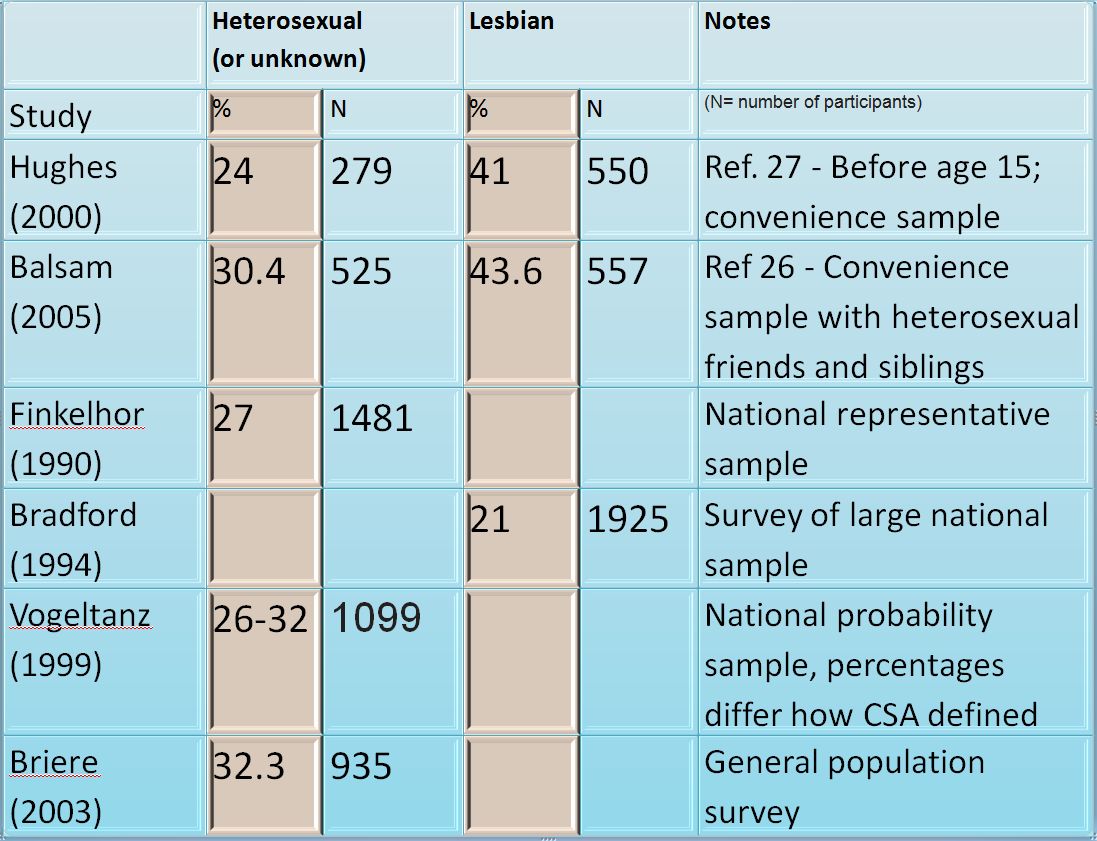
A look at the table demonstrates that most research finds a modest elevation for lesbians but does not demonstrate the 50% figure nor support for the conclusion that prevalences are twice as high for lesbians as straight women. Prevalences are sadly and unacceptably high for all women.
I fear that this fact sheet will become basis for inaccurate information spread by sexual identity and ex-gay ministries. Whatever the reason for the differences, it cannot be helpful to paint a false picture. Sexual abuse is a trauma that often requires therapeutic and spiritual intervention but whether it is involved in the origins of same-sex attractions continues to be an open question.
References:
Balsam, K.F.; Rothblum, E.D., & Beauchaine, T.P. (2005). Victimization over the life span: A comparison of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and heterosexual siblings. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 73, 477-487.
Bradford, J., Ryan, C., & Rothblum, E.D. (1994). National lesbian health care survey: Implications for mental health care. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62, 228-242.
Briere, J., & Elliott, D. M. (2003). Prevalence and psychological sequelae of self-reported childhood physical and sexual abuse in a general population sample of men and women. Child Abuse & Neglect. 27, 1205-1222.
Finkelhor, D., Hotaling, G., Lewis, I.A., & Smith, C. (1990). Sexual abuse in a national survey of adult men and women: Prevalence, characteristics, and risk factors. Child Abuse & Neglect. 14, 19-28.
Hughes, T.L., Haas, A.P., Razzano, L., Cassidy, R., & Matthews. A. (2000). Comparing lesbians and heterosexual women’s mental health: Results from a multi-site women’s health survey. Journal of Gay and Lesbian Social Services, 11 (1), 57-76
Peters, D. & Cantrell, P. (1991). Factors distinguishing samples of lesbian and heterosexual women. Journal of Homosexuality, 21, 1-15.
Vogeltanz, N.D., Wilsnack, S.C., Harris, T. R., Wilsnack, R.W., Wonderlich, S.A., & Kristjanson, A.F. (1999). Prevalence and risk factors for childhood sexual abuse in women: National survey findings. Child Abuse & Neglect. 23, 579-592.
ok. I have not really looked at all these messages to get everyones whole story, but if they say women are “gay” because of sexual abuse. Then whats the resoning for all the women who were not abused?
please write back,
thanx
being abused as a child does not correspond in any way to a person’s sexual orientation… There are many other factors which contribute.such people may undergo in their lives some phases in which they may try and experience homosexual behavior but this does not reflect their true needs in the long run and sooner or later they come back to usual. it’s obvious that sexual behavior or history of a person’s sexual life may not necessarily indicate thier orientation. plus, just by the way, all the statistics are bullcrap as many many ppl never take pare in such a survey. there are many homosexuals (men and women) living their lives in the closet, having normal families and normal family background with no abuse.
Sexual orientation is formed very earily which means that neither a person can be born gay nor is a choice. it must be somehow shaped in the very first years of life and what is considered generally as ‘sexual orientation’ consists of :
-emotional orientation
-romantic orientation
-erotic orientation
but not purely ‘sexual ‘- in the meaing of ‘biological’ orienation because from biological point of view there is no instinctive biological sexual attraction towards the same sex.this what is called ‘homosexal orientation’ is shaped later, after birth on psychological grounds and it’s significantly affected by self identification as a woman or man.
Just skimmed the commentaries this post ellicited.
One of the problems seem to be speculating over which parent is or isn’t detached from.
In my experience, people who feel CSA has made a huge, lasting, impact, also feel there was general lack of attachments in their life.
Those who had loving parents feel CSA, though influential in negative and lasting ways, not so much. Less issues with drugs, addictive behaviors, etc… And, I would imagine, less likely to be impacted in their sexual development.
So I’m not sure the debate is really one of “did it make you gay or straight”, but the ways in which it impacted the ability to form stable attachments, and where stable attachments are weak or missing ,then how this was expressed sexually.
It seems to me that a lot of sexual abuse victems are not overly concerned with which sex turns them on the most — but which sex seems less scary, and which more scary.
Safety seems more important than attraction in a more overt, on-going -concern, sort of way.
And it was interesting for me to read Arugala Rose’s comments regarding the necessity to study one’s environment and copy it rather than getting it early on and just living in it. I had a longer than average time doing this in order to figure out how to live my gender.
Seems to me that the whole straight/gay thing can lead us to overlook things like this.
K.
In my case, childhood sexual abuse caused me to be straight. I was raped as a young girl and have spent my whole life trying to “prove” that my sexuality was intact. But, not really knowing what an intact sexuality looked like, and being completely dissociated from my own body, I turned to cultural models about sex which of course are all heterosexual. This led me to ignore, disregard etc. all of my erotic feelings towards women as I entered into one after another unstable relationship with men. Through therapy I see the role of that trauma in making me straight. Without therapy and the loving support of my friends I would never recognize how that violation has set me up for loss over my whole life. I would probably live my whole life and die still identifying as heterosexual if I weren’t uncovering this abuse now. It makes me want to cry and cry and cry, to have lost so many years of connection with my own desire.
Katie,
There a few unknowns on this issue. Like:
– Do the same men and women react the same in time? That is, if someone goes through the same procedures in different weeks and months, do they get the same result? That’s too expensive to find out with brainscans..
– Do the same men and women react the same to a large variety of stimuli, given extended time? For instance, could a gay man be attracted to a smaller and shyer woman and a straight man to a more dominant man, but on average remain more attracted to their preferred sex? and
– Why do most gay men prefer passive stimulation? The physiology of arousal is different from that of “straight” men? Likely to be so.
Getting some answers to these questions and seeing how much flexibility is there would really help people understand how many of the things they think are only typical for certain orientations are actually normal, widespread… And how many are really typical, ofc.
Just want to say, I’m no fan of NARTH.
And also, just like many women who turn away from penetrative sex, many male CSA victims abhore the thought of using their penises in a penetrative fashion.
To me, it seems that ignoring subjective reports requires having EXTREMELY good reasons to do so.
So again, based on what measurements is it “proven” that men’s brains don’t respond to stuff like this in an analogous way — realizing that all analogies fail at some point, and my question do NOT need to assume that there are NO differences between male and female brains, because there certainly is some, otherwise our brains couldn’t help direct the development of different morphologies.
Still, that subjective experience is questioned when it comes to me because of some measurement is highly questionable, unless that measurement cannot itself be questioned. And I doubt this is the case.
Katie
Plethysmograph and some brain scanning work. The brain scan work is very clear as is some perceptual work out of Minnesota. When I get time later, I will put some references down.
What is your take on the matter?
Happened to have pulled this old thread up while doing a broader search, but thought I’d ask Warren:
Based on what sort of measurement is it found that men do NOT respond in any way to both male and female stimuli?
That’s my first question.
I have yet to come across a very good argument for this, and lots of observation that this isn’t quite right, and the problem is the standard of measurement.
Katie
Am I missing the point – is the thread a NARTH bashing or are we discussing women with SSA and sexual abuse and how NARTH has presented the information and what can be gleaned from that?
Why should it be “wiring” that NARTH has to explain. Is it not simply “thinking” that NARTH is concerned with? I’d think that would be NARTH’s viewpoint, especially a Nicolosi who says that once a guy realizes the problem is with his relationship with his father then the homosexuality goes away. You cannot re-wire a brain that fast, can you? Even easier than my house.
Which is to say that their whole argument sounds so illogical except to anyone who is desperate for change.
Warren,
Did miss what you were saying?
Warren,
We are talking about women, correct? Women re different on this issue – just because we classify homosexuality into one topic does not mean that gay men and women are the same.
Their hyperbole is worse than might happen in a high school term paper.
For women, the brain may not have a change but for men, the brain is clearly reacting the same way to different cues.
If the NARTH theory was true for men, that everybody starts straight and some become gay due to detachment from the same-sex parent then we would need a plausible theory about how that detachment changes the course of brain wiring so that attraction to men is so automatic and natural.
Warre,
i don’t thnk it does hard wire the brain. I think women see it a viable alternative to get their needs met without more exposure to more male sexual abuse. So, if this is the most contributing factor – women like myself respond better to therapy.
Mary – We have data to suggest 60+% of the difference between gay and straight people relate to varied experiences, as CSA would be. And so, I do not doubt that for some, CSA is life altering. What we do not know is how CSA would wire brains to find the same-sex attractive in the same way that straight people find the opposite sex attractive.
For women, this probably isn’t as difficult since most women can be sexual aroused by both SS and OS triggers. The attachment issue (or detachment from men as another way of saying it) seems more important for women and is consistent with your testimony.
Warren,
Understandable and yet, we still hav a small group of people to look at and with the APA in the way with their “doctrine”. People have to sart somewhere. I don’t like the lack of reiable reserch either.
The reason for putting my personal experience out there is to be a voice and say “Yes, that was my experience.” Many people will read your critique and conclude that sexual abuse is not part of the experience of women with SSA.
But for this woman it is. I am saying it clearly -it may not be the exerience of all SSA women. I don’t want to diminish in anyway the contribution that so far has been made to the research and evaluation of SSA in women. Women with SSA have been largely overlooked and finding material on the subject is not easy. Especially when some female authors spend too much time on the religious/ theology aspect of SSA.
Though the data provided come from a convience source – it is a start and worth looking at.
Yes, this woman was sexually abused and that abuse contributed to SSA. So, that is relevant. Not perfect – but relevant.
I think this paper on female SSA is an improvement for NARTH, but they still have a long way to go.
I think the premise that CSA among SSA women is higher than OSA women is a reasonable, modest assertion. As well as perhaps a triggering event for some women in ultimately pursuing SSA.
The article, however, does not note the more obvious fact that OSA and SSA women have more in common: Clear majorities have never been sexually abused.
MORE IMPORTANT:
Papers like this are clearly important efforts to present information, but the WEAK Citations coupled with the EXAGGERATION of the weak citations, is very troubling.
This HAPPENS WITH ADVOCACY! And is prevalent in the advocacy papers submitted in the last generation by HRW and FOTF.
ADVOCACY tries to talk like science and thereby DECIEVES.
*capital letters in this post suggest strong feelings of either outrage or disgust.
My objections to the NARTH fact sheet has more to do with it not containing many facts, not that CSA is unimportant in the formation in sexuality.
What NARTH does is to link research studies having nothing to do with homosexuality with their theoretical views and call this fact. If that fact sheet was a paper for a class at GCC, it would get a C-/D+.
Nonetheless, while research is not present I can say in my situation that sexual abuse was the last straw in a series of events that moved me in the direction of lesbianism. It was not the ONLY factor – and I believe others were in place – but it is definitely a factor that contributed to my SSA. Simply, I was tired of having penises forced on me and yet, I wanted intimacy – without penises was my thinking at the time. I was just a girl and had no skills for managing or coping with sexual abuse.